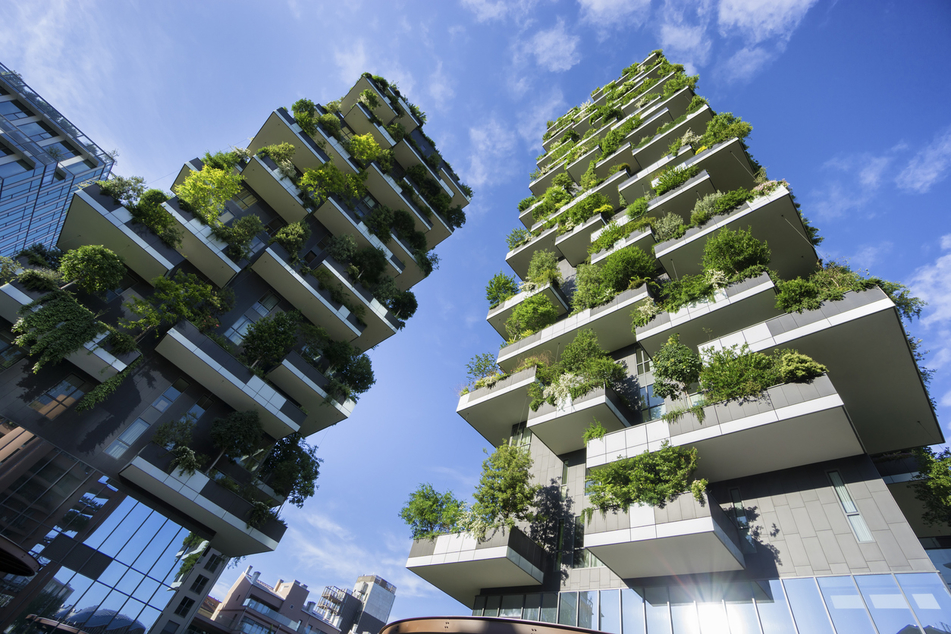
If you’re looking to make the most of your gardening space and increase your yield, then vertical gardening might be just the solution for you. With vertical gardening, you can transform any small or limited area into a thriving, productive garden. By utilizing wall space, trellises, and hanging structures, vertical gardening allows you to grow a wide variety of plants while optimizing space. Whether you have a tiny balcony or a sprawling backyard, vertical gardening offers a practical and innovative way to maximize your gardening potential.

This image is property of www.permaculturenews.org.
Benefits of Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening is a great solution for individuals who have limited space but still want to enjoy the benefits of gardening. By utilizing vertical structures, you can make the most out of your available space, whether it’s a small backyard, balcony, or even indoor area.
Utilizing limited space
One of the biggest advantages of vertical gardening is its ability to make use of limited space. Traditional gardening methods often require a large plot of land, which can be a challenge for those living in urban areas or small apartments. However, with vertical gardening, you can grow plants upwards instead of outwards. This allows you to make the most of your available space by utilizing walls, fences, or even hanging structures.
Vertical gardening is also a great solution for those with limited mobility or physical disabilities. With the plants at eye level or within easy reach, it eliminates the need for bending or kneeling down, making gardening more accessible and enjoyable for everyone.
Maximizing yield
Vertical gardening not only allows you to make the most of your limited space but also enables you to maximize your yield. By growing plants vertically, you can increase the number of plants you can grow in a given area. This means more fruits, vegetables, flowers, and herbs for you to enjoy.
Furthermore, vertical gardening provides an opportunity to grow a variety of plants simultaneously. With different levels and tiers, you can create a diverse garden with a mix of climbing vines, compact plants, and even shade-tolerant varieties. This variety not only adds visual interest to your garden but also ensures a continuous harvest throughout the season, providing you with a steady supply of fresh produce.
Reduced risk of pests and diseases
Another significant benefit of vertical gardening is its ability to reduce the risk of pests and diseases. When plants are grown vertically, they are naturally less susceptible to ground-dwelling pests and soil-borne diseases. This is because pests and diseases often reside or spread near the ground, making it more challenging for them to reach vertically grown plants.
Additionally, the vertical orientation of the garden allows for better airflow and sunlight exposure, which helps prevent the development of fungal diseases. Adequate airflow helps to keep the leaves dry, reducing the chances of mold or mildew growth. This, in turn, leads to healthier plants and fewer issues with pests and diseases.
Choosing the Right Vertical Structures
When it comes to vertical gardening, selecting the right structures is crucial to the success of your garden. The choice of structures will depend on the available space, aesthetic preferences, and the types of plants you plan to grow. Here are three common types of vertical structures to consider: trellises, vertical towers, and living walls.
Trellises
Trellises are an excellent choice for those who want to grow climbing or vining plants such as cucumbers, tomatoes, or grapes. These structures provide support for the plants, allowing them to grow vertically and encouraging better airflow and light penetration.
Trellises come in various materials like wood, metal, or even recycled materials such as PVC pipes. You can choose a pre-made trellis or create your own using wire mesh, bamboo, or wooden stakes. Whichever material you choose, make sure it is sturdy enough to withstand the weight of the plants and weather conditions.
Vertical towers
Vertical towers, also known as vertical planters or garden towers, are a great option for those with limited floor space. These towers consist of multiple levels of planting pockets or pots stacked vertically, allowing you to grow a large number of plants in a small footprint.
Vertical towers are versatile and can accommodate a wide range of plants, including herbs, flowers, and even small vegetables. Many vertical tower systems also incorporate a built-in irrigation system, making them ideal for those who want a low-maintenance gardening solution.
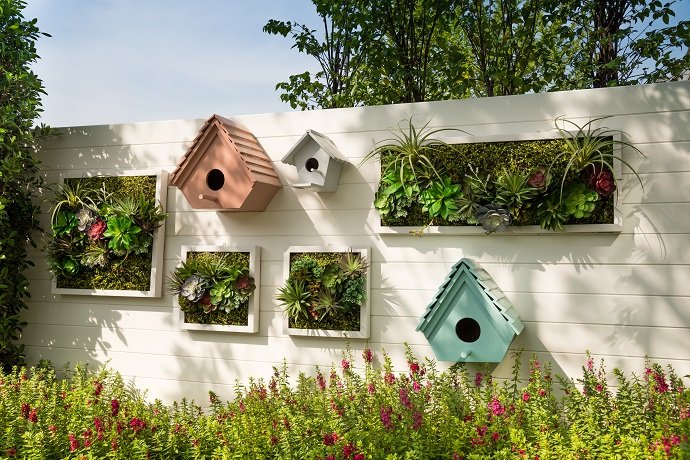
Living walls
Living walls, also called green walls or vertical gardens, are a captivating and space-saving option for both indoor and outdoor gardening. These structures consist of plants attached to a vertical surface, creating a living tapestry of foliage and flowers.
Living walls can be made using modular systems, where individual plant modules are attached to a frame, or by creating a custom structure using planters or containers attached to a wall. Keep in mind that living walls require careful consideration of watering and drainage to prevent oversaturation or water damage to the underlying structure.

This image is property of www.permaculturenews.org.
Selecting Suitable Plants
When it comes to vertical gardening, selecting the right plants is key to ensuring a thriving garden. Different plants have varying growth habits, light requirements, and space needs. Here are a few tips on selecting suitable plants for your vertical garden:
Shade-tolerant plants
If your vertical garden is located in a shaded area, it’s essential to choose plants that can thrive with limited sunlight. Fortunately, many plants are shade-tolerant and can still produce decent harvests with indirect or filtered light. Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and kale are excellent choices for shaded vertical gardens.
Other options for shade-tolerant plants include ferns, herbs like mint and parsley, and certain flowering plants such as impatiens or begonias. It’s crucial to assess the light conditions in your garden before selecting plants to ensure they will receive adequate light for their growth.
Vining plants
Vining plants are a natural fit for vertical gardens, as their climbing habit allows them to take advantage of the vertical space. Examples of vining plants include cucumbers, beans, peas, and various types of melons. These plants can be trained to grow along trellises, vertical towers, or other structures, providing a beautiful and productive display.
When selecting vining plants, consider the available height and ensure the structure can support their growth. Some vining plants require robust trellises or support systems, while others can thrive in more compact vertical towers.
Compact plants
Compact plants are ideal for vertical gardens with limited space or those that don’t provide optimal growing conditions. These plants tend to have a bushy or dense growth habit and don’t require as much space as their larger counterparts. Compact tomatoes, peppers, herbs like thyme or oregano, and even dwarf varieties of fruit trees are excellent choices for vertical gardens.
Compact plants often perform well in containers or smaller spaces, making them suitable for indoor vertical gardens or balconies. Their smaller size also makes them easier to manage and maintain, allowing you to make the most out of your vertical garden.
Preparing the Vertical Garden
Before you start planting, it’s crucial to prepare your vertical garden properly. Proper preparation ensures that your garden has a solid foundation for healthy growth and reduces the risk of potential issues.
Determining the location
The location of your vertical garden plays a significant role in its success. Choose an area that receives adequate sunlight for the plants you intend to grow. Most edible plants require a minimum of six hours of direct sunlight per day, while some shade-tolerant plants can still thrive in areas with indirect or filtered light.
Consider factors such as access to water, protection from strong winds, and the weight-bearing capacity of the chosen structure. If you’re growing a vertical garden indoors, ensure that the chosen location has suitable ventilation and access to natural or artificial light sources.
Preparing the support structures
Before installing your vertical structures, make sure they are stable and securely fastened to avoid any collapse or damage to your plants. For freestanding structures like trellises or vertical towers, ensure they are anchored to the ground or secured against a wall or fence.
Inspect each component for stability and durability, especially if you’re using pre-made structures. If you’re building your own structures, ensure that the materials can withstand the weight of the plants and have proper reinforcement or bracing as needed.
Creating proper drainage
Proper drainage is crucial for the health of your plants in a vertical garden. Excess water should be able to flow freely out of the planters or containers to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Ensure your vertical structures have adequate drainage holes or a system in place to allow for proper water flow.
Consider using a high-quality potting mix or soil specifically formulated for container gardening. These mixes provide good drainage while still retaining enough moisture for your plants. Additionally, placing a layer of small stones or pebbles at the bottom of your planters can help with drainage by creating a space for excess water to collect.

This image is property of www.epicgardening.com.
Vertical Garden Growing Techniques
Vertical gardening offers various techniques for growing plants, allowing you to choose the method that suits your preferences and needs. Here are a few popular techniques commonly used in vertical gardens:
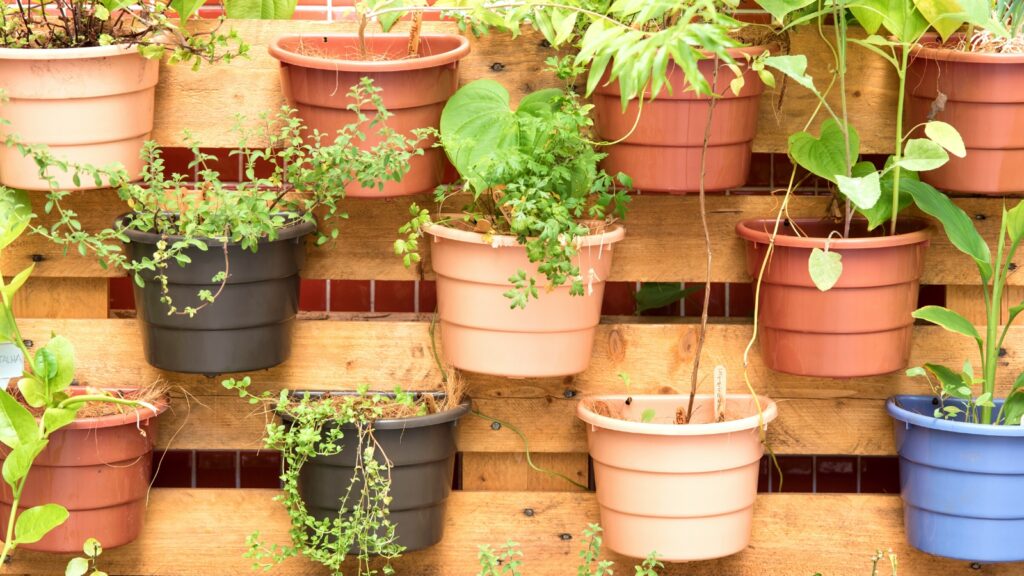
Container gardening
Container gardening is a versatile and widely used technique in vertical gardens. It involves growing plants in containers or pots filled with a suitable growing medium such as potting soil or a soilless mix. Containers can be placed on shelves, hung from structures, or stacked in vertical towers.
Container gardening allows for easy mobility and flexibility, making it ideal for those who have limited space or want to bring their garden indoors during colder months. It also enables you to control the growing conditions more effectively, including soil quality, moisture levels, and fertilization.
Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soilless growing system that uses a nutrient-rich water solution to provide plants with the necessary nourishment. In a vertical hydroponic system, plants are typically grown in individual net pots or slots, held vertically in a tower or vertical gardening structure.
This technique allows plants to take up water and nutrients more efficiently, resulting in faster growth rates and higher yields. Hydroponics also minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases and simplifies soil management. Although hydroponic systems require more initial setup, they offer precise control over plant nutrition and can be ideal for those interested in maximizing space and yields.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is an advanced vertical gardening technique that involves growing plants with their roots suspended in air and misted with a nutrient-rich mist. This method provides plants with a highly oxygenated and well-aerated environment, allowing for rapid growth and efficient nutrient uptake.
Aeroponics systems typically consist of vertical structures with individual plant sites or a central nutrient delivery system. This technique offers several advantages, including faster growth rates, higher yields, and reduced water consumption compared to traditional gardening methods. However, aeroponics requires more precise monitoring and control of the growing environment, making it better suited for experienced gardeners or commercial operations.
Irrigation and Fertilization Methods
To ensure the health and productivity of your vertical garden, proper irrigation and fertilization are essential. Here are a few methods commonly used in vertical gardens:
Drip irrigation
Drip irrigation is a popular and efficient method for watering plants in vertical gardens. It involves the use of a network of tubes or pipes with small emitters that deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone.
Drip irrigation minimizes water wastage by delivering water precisely where it is needed, reducing runoff and evaporation. By keeping the leaves dry and watering directly at the root level, drip irrigation also helps prevent the spread of fungal diseases. It’s a convenient option, especially for larger vertical gardens or those with water restrictions.
Watering systems
Various watering systems can be used in vertical gardens, depending on the size and complexity of the garden. Some systems include automated timers or sensors to ensure consistent watering.
For smaller vertical gardens, handheld watering cans or spray bottles can be sufficient for watering. Additionally, self-watering containers or planters with built-in reservoirs are available, providing a continuous water supply for the plants.
Organic fertilizers
To nourish your plants and promote their growth, organic fertilizers are an excellent choice for vertical gardens. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and provide a slow-release of nutrients, ensuring a steady supply for the plants.
Compost, worm castings, and organic plant-based fertilizers are commonly used in vertical gardens. These fertilizers not only provide essential nutrients but also help improve soil structure, water retention, and overall soil health. Remember to follow the recommended application rates for each fertilizer to avoid over-fertilization and potential damage to your plants.

This image is property of themicrogardener.com.
Pest and Disease Management
Although vertical gardening reduces the risk of pests and diseases compared to traditional gardening methods, it’s still essential to implement pest and disease management techniques. Here are a few strategies to consider:
Companion planting
Companion planting is a technique that involves planting certain plants together to benefit each other in terms of pest control. Some plants have natural properties that repel pests or attract beneficial insects, which can help protect your vertical garden.
For example, planting marigolds near your vertical garden can repel pests like aphids, while attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs that feed on harmful pests. Similarly, planting herbs like basil, rosemary, or mint can deter pests and provide additional culinary value.
Natural repellents
If pests still become a problem in your vertical garden, natural repellents can help deter them without the use of harmful chemicals. Some natural repellents include neem oil, garlic spray, or chili pepper spray. These can be applied directly to plants or around the garden area to deter pests.
It’s important to note that even natural repellents should be used sparingly and following the recommended application rates. Always test these repellents on a small area or a single plant first to ensure they don’t cause any adverse effects.
Regular monitoring
Regular monitoring is crucial for early pest or disease detection in your vertical garden. Inspect your plants regularly for signs of damage, unusual growth, or discoloration. Look for pests such as aphids, caterpillars, or spider mites, as well as any signs of fungal diseases like powdery mildew or leaf spots.
If pest or disease infestations are detected, take immediate action to prevent them from spreading further. This can include handpicking pests, removing infected plant parts, or using organic pest control methods.
Harvesting and Maintenance
Harvesting and maintenance are essential aspects of vertical gardening to ensure continued productivity and healthy plant growth. Here are some guidelines to follow:
Harvesting techniques
When it comes to harvesting your vertical garden, proper techniques are essential to avoid damage to the plants and ensure continued growth. For fruits and vegetables, harvest them when they are ripe or slightly underripe for the best flavor and quality.
When harvesting leafy greens or herbs, gently snip off the outer leaves or stems, leaving the inner growth intact. This allows the plant to continue growing and producing. Avoid harvesting more than one-third of the plant’s foliage at once to maintain its health and vigor.
Pruning and trimming
Regular pruning and trimming are necessary to maintain the shape and size of your plants in a vertical garden. Remove any dead or diseased plant parts promptly to prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
For vining plants, pruning can help control their growth and improve airflow, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Monitor your plants regularly and trim back any excessively long or unruly growth. Pruning can also promote bushier growth and encourage the development of more side shoots or flowers, resulting in a more productive plant.
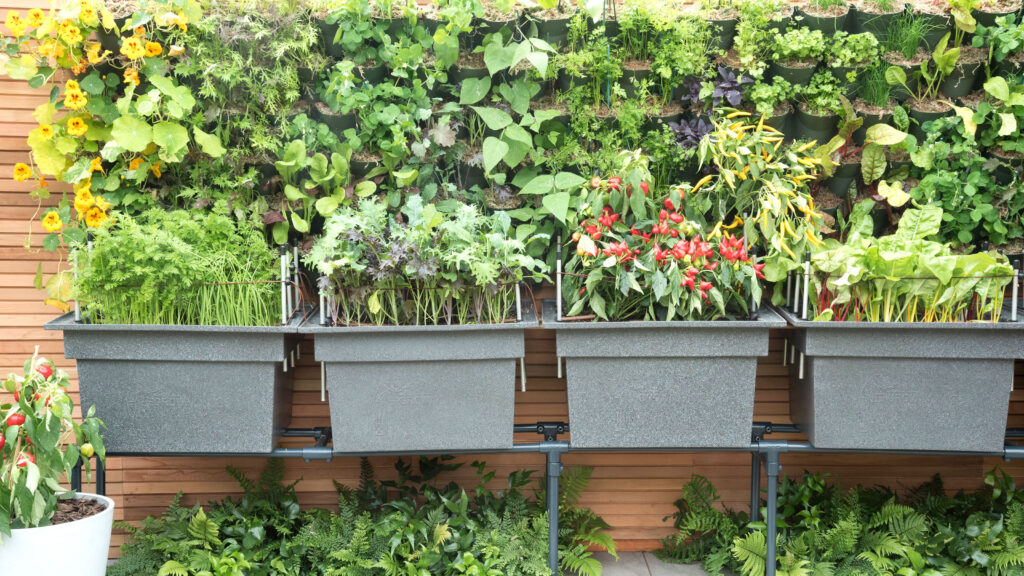
Weed control
Weed control is crucial in any garden, including vertical gardens. Weeds compete with your plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight, hampering their growth and productivity. Regularly inspect your vertical garden for any weed growth and remove them promptly.
To prevent weed growth, consider using organic mulches like straw, wood chips, or compost. These help suppress weed growth, retain soil moisture, and add nutrients to the soil as they decompose. Be careful not to apply mulch too close to the base of the plant to prevent any rot or fungal issues.

This image is property of cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net.
Utilizing Vertical Gardens in Urban Spaces
Vertical gardening is especially beneficial in urban spaces where land may be a limited resource. Here are a few ways to utilize vertical gardens in urban areas:
Community gardens
Community gardens are a fantastic way to bring people together and create a shared space for urban gardening. Vertical gardens can be incorporated into community garden projects, allowing individuals to grow their own food or beautify the space collectively. These gardens can be constructed on walls, fences, or freestanding structures, enabling residents to maximize their available space.
Roof gardens
Roof gardens, also known as rooftop gardens or green roofs, transform unused or underutilized roof spaces into vibrant green spaces. Vertical gardening techniques can be combined with rooftop gardens to create stunning and productive spaces in urban environments.
Roof gardens provide many benefits, including insulation, stormwater management, and urban heat island mitigation. They can also improve air quality and provide habitat for wildlife. Vertical gardens on rooftops make use of the vertical space, maximizing the gardening potential and adding visual interest to the landscape.
Indoor vertical gardens
Indoor vertical gardens are a fantastic option for those who have limited outdoor space or want to bring nature indoors. These gardens can be created using various vertical structures and can range from small herb gardens in the kitchen to large living walls in commercial spaces.
Indoor vertical gardens contribute to cleaner air, increased humidity, and a more serene and inviting environment. They also provide easy access to fresh herbs or greens for cooking, even in the middle of a bustling city. With the right combination of vertical structures, suitable plants, and proper lighting, indoor vertical gardens can thrive year-round.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Vertical garden in a small apartment balcony
Sarah, a city dweller with a small apartment balcony, transformed her limited outdoor space into a thriving vertical garden. She utilized a combination of trellises and vertical towers to maximize her planting area. Sarah grew a variety of vining plants such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and pole beans, training them to grow vertically on the trellises. On the vertical towers, she planted herbs like basil and mint, as well as compact lettuce varieties. Despite her limited space, Sarah harvested an abundant supply of fresh produce, bringing vibrancy and nature to her urban living.
Commercial vertical farming operation
In a bustling city center, a commercial vertical farming operation flourishes, providing fresh greens and herbs to local restaurants and consumers. By utilizing hydroponic and aeroponic systems, the farmers maximize their crop yields and utilize their space more efficiently. The plants grow vertically, supported by meticulously designed structures. The use of advanced irrigation and fertilization systems ensures optimal growing conditions and minimal water consumption. This commercial vertical farming operation serves as a sustainable and innovative solution to bring fresh produce to urban areas, reducing food miles and promoting local food production.
Vertical garden in a school
At Greenlake Elementary School, a vertical garden thrives, providing a hands-on learning experience for the students. Through a collaboration between parents, teachers, and local gardening organizations, the school transformed a bare wall into a living tapestry of plants. The vertical garden serves as an outdoor classroom, teaching the students about plant life cycles, nutrition, and sustainability. Students are actively involved in maintaining the garden, from planting seeds to harvesting the fruits and vegetables. The vertical garden not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the school but also promotes environmental stewardship and healthy eating habits among students.
In conclusion, vertical gardening offers numerous benefits and opportunities for individuals and communities in utilizing limited space, maximizing yield, and reducing the risk of pests and diseases. By choosing the right vertical structures, selecting suitable plants, preparing the garden properly, and implementing the right growing techniques, irrigation and fertilization methods, and pest and disease management strategies, you can create a thriving and productive vertical garden. Whether in urban spaces, community gardens, or commercial operations, vertical gardening provides a sustainable and innovative solution to maximize space and yield, bringing nature and horticultural joy to all.